23 Section 5.2 Polynomials
a. A polynomial, [latex]h[/latex], with degree 5, a zero at [latex]x=-1[/latex] with multiplicity 3, and zeros of multiplicity 1 at [latex]x=2[/latex] and [latex]x=5[/latex]. This polynomial passes through [latex](1,16)[/latex].
b. A polynomial, [latex]k[/latex], with degree 6, zeros of multiplicity 2 at [latex]x=-4[/latex] and [latex]x=1[/latex], and zeros of multiplicity 1 at [latex]x=0[/latex] and [latex]x=-6[/latex]. This polynomial passes through [latex](-1,28)[/latex].
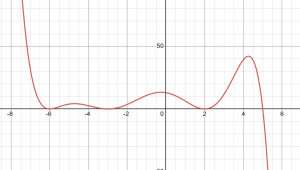
c. A polynomial that represents the graph of [latex]m[/latex] below, with a vertical intercept of 13. The polynomial should have the lowest degree possible.
Show Solution
Answers
a. First, start writing the zeros into the polynomial form: [latex]h(x)=a(x+1)^3(x-2)(x-5)[/latex]. Since this function must pass through [latex](1,16)[/latex], we then must calculate the [latex]a[/latex] value. Substitute [latex]x=1[/latex] and set the equation equal to [latex]16[/latex].
[latex]16=a(1+1)^3(1-2)(1-5)[/latex]
[latex]16=a(2)^3(-1)(-4)[/latex]
[latex]a=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
Thus, a polynomial that fits these characteristics is [latex]h(x)=\frac{1}{2}(x+1)^3(x-2)(x-5)[/latex].
b. Starting with the zeroes, [latex]k(x)=ax(x+4)^2(x-1)^2(x+6)[/latex]. Then, we calculate the [latex]a[/latex] value by substituting [latex]x=-1[/latex] and [latex]y=28[/latex].
[latex]28=a(-1)(3)^2(-2)^2(5)[/latex]
[latex]28=a(-180)[/latex]
[latex]a=\frac{28}{-180} =-\frac{7}{45}[/latex]
Thus, a polynomial that fits these characteristics is [latex]k(x)=-\frac{7}{45}x(x+4)^2(x-2)^2(x+6)[/latex]
c. To write a polynomial for this graph, start with the possible degree. Given the end behavior and the number of zeros with their multiplicities, this polynomial must be of degree at least 7. The zeros at [latex]x=-6[/latex], [latex]x=-3[/latex] and [latex]x=2[/latex] have even multiplicity, so we will assume that they are multiplicity 2 for now. The zero at [latex]x=5[/latex] has multiplicity 1. All of this information gives:
[latex]m(x)=a(x+6)^2(x+3)^2(x-2)^2(x-5)[/latex]
Then, knowing the vertical intercept of 13, find [latex]a[/latex].
[latex]13=a(0+6)^2(0+3)^2(0-2)^2(0-5)[/latex]
[latex]13=a(-6480)[/latex]
[latex]a=-\frac{13}{6480}[/latex]
Thus, a polynomial representing the graph is [latex]m(x)=-\frac{13}{6480}(x+6)^2(x+4)^2(x-2)^2(x-5)[/latex].