2.1 Traversing Circles
Activity 2.1.2
Consider the circle pictured in Figure 2.1.6 that is centered at the point (2, 2) and that has circumference Assume that we track the -coordinate (that is, the height, [latex]h[/latex]) of a point that is traversing the circle counterclockwise and that it starts at [latex] P_{0}[/latex] as pictured.
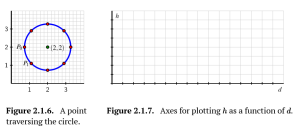
a. How far along the circle is the point [latex]P_{1}[/latex] from [latex]P_{0}[/latex] Why?
b. Label the subsequent points in the figure [latex]P_{2}[/latex], [latex]P_{3}[/latex] as we move counterclockwise around the circle. What is the exact -coordinate of the point [latex]P_{2}[/latex] of [latex]P_{4}[/latex] Why?
c. Determine the [latex]y[/latex]-coordinates of the remaining points on the circle (exactly where possible, otherwise approximately) and hence complete the entries in Table 2.1.8 that track the height, [latex]h[/latex], of the point traversing the circle as a function of distance traveled, [latex]d[/latex]. Note that the [latex]d[/latex]-values in the table correspond to the point traversing the circle more than once.
d. By plotting the points in Table 2.1.8 and connecting them in an intuitive way, sketch a graph of [latex]h[/latex] as a function of [latex]d[/latex] on the axes provided in Figure 2.1.7 over the interval [latex]0\leq d \leq 16[/latex]. Clearly label the scale of your axes and the coordinates of several important points on the curve.
e. What is similar about your graph in comparison to the one in Table 2.1.5? What is different?
f. What will be the value of [latex]h[/latex] when [latex]d=51[/latex] How about when [latex]d=102[/latex]
Show Solution
a. Since there are 8 segments in this circle and the circumference is 8, the distance from each point to the next is 1.
b.
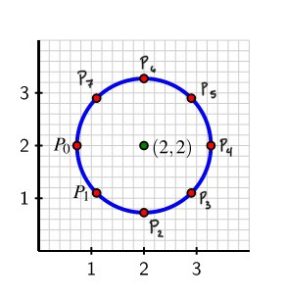
To find the [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate of [latex]P_{2}[/latex], we first need the radius of the circle. Use the circumference formula: [latex]C=2\pi r[/latex].
[latex]8=2\pi r[/latex]
[latex]r=\frac{4}{\pi}[/latex]
So the radius is [latex]\frac{4}{\pi}[/latex]. This means that we can find the [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate of [latex]P_{2}[/latex] by looking at the [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate of the center, 2, and subtracting the radius value. This means that the [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate of [latex]P_{2}[/latex] is [latex]2-\frac{4}{\pi}[/latex].
For [latex]P_{4}[/latex]'s [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate, notice that [latex]P_{4}[/latex] is directly horizontal from the center of the circle [latex](2,2)[/latex]. This means the [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate of [latex]P_{4}[/latex] is 2.
c.
![]()
The [latex]h[/latex]-values of 1.1 and 2.85 were found by estimating from the graph.
d.
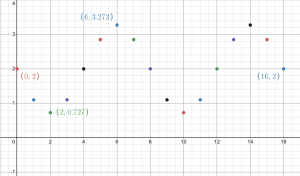
e. It has clear periodic peaks and troughs, but does not touch the [latex]x[/latex]-axis, ie ever have a height of 0.
f. For [latex]d=51[/latex], [latex]h[/latex] will be 1.1. This is because a distance of 51 means that you've gone around the circle 6 full times (48 segments), then advance 3 more segments to be at [latex]P_{3}[/latex], which has a [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate of 1.1.
For [latex]d=102[/latex], [latex]h[/latex] will be [latex]2+\frac{4}{\pi}[/latex]. To get to a distance of 102 means that you have gone around the circle 12 full times (98 segments), then go 6 more segments to be at [latex]P_{6}[/latex], which has a [latex]y[/latex]-coordinate of [latex]2+\frac{4}{\pi}[/latex].
A weight is placed on a frictionless table next to a wall and attached to a spring that is fixed to the wall. From its natural position of rest, the weight is imparted an initial velocity that sets it in motion. The weight then oscillates back and forth, and we can measure its distance, [latex]h=f(t)[/latex] (in inches) from the wall at any given time, [latex]t[/latex] (in seconds). A graph of [latex]f[/latex] and a table of select values are given below.
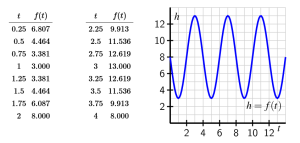
a. Determine the period [latex]p[/latex] midline [latex]y=m[/latex] and amplitude [latex]a[/latex] of the function [latex]f[/latex].
b. What is the furthest distance the weight is displaced from the wall? What is the least distance the weight is displaced from the wall? What is the range of [latex]f[/latex]
c. Determine the average rate of change of[latex]f[/latex] on the intervals and Write one careful sentence to explain the meaning of each (including units). In addition, write a sentence to compare the two different values you find and what they together say about the motion of the weight.
d. Based on the periodicity of the function, what is the value of [latex]f(6.75)[/latex] of [latex]f(11.25)[/latex]
Show Solution
a. [latex]p=4[/latex]. midline: [latex]y=8[/latex]. [latex]a=5[/latex].
b. The furthest distance is 13 (largest [latex]f(t)[/latex] value in the table, on the graph). The least distance is 3 (smallest [latex]f(t)[/latex] value in the table, on the graph).
Range: [latex][3,13][/latex]
c. SKIP
d. [latex]f(6.75)=12.619[/latex]. This is because [latex]t=6.75[/latex] corresponds to [latex]t=2.75[/latex] after traveling through one period of 4 units. Then reference the given table.
[latex]f(11.25)=12.619[/latex]. This is found by cycling through two period of 4, ie 8 units, to land at [latex]t=3.25[/latex]. Then reference the given table.
